Methods to treat HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) have improved greatly since the virus first began to affect humans, in the late 1980s. A few of those infected never developed full-blown AIDS, but for the majority, the inevitable result would have been wasting away due to an inability to fight diseases. Treatment for HIV has improved continuously, and the disease is no longer considered to be fatal once the affected person receives treatment. These treatments have at least two disadvantages, however: they would need to be continued for the duration of the individual’s lifetime and there are also uncomfortable side effects. Researchers are confident that there will eventually be a cure for HIV, and they continue to do tests that may take us closer to finding one.
 Scientists from The University of Massachusetts Medical School have published an article in Nature, which states the possibility of decreasing the spread of HIV using cells which occur naturally in our bodies. Ironically, these are the same cells which the virus attacks. HIV breaks down the immune system by infecting and destroying CD4 positive ‘helper’ T-cells.
Scientists from The University of Massachusetts Medical School have published an article in Nature, which states the possibility of decreasing the spread of HIV using cells which occur naturally in our bodies. Ironically, these are the same cells which the virus attacks. HIV breaks down the immune system by infecting and destroying CD4 positive ‘helper’ T-cells.
These white blood cells are vital to fighting off infection, which is why HIV is so efficient at wrecking havoc in the immune system. After affecting some of the cells, the virus uses these to travel through the body and infect other CD4s. T-cells transport these by settling in between lymph nodes, and others areas, that the free virus would be unable to reach.
 The researchers found that there are proteins in the T-cells in our immune system which naturally fight HIV. SERINC5 and SERINC3, two host cell proteins, are able to stifle HIV-1 by greater than 100-fold. The HIV-1 genome has nine genes which can be replicated in the host cell, which then produce virions (the infectious part of the virus). They begin a cycle of infection by looking for new cells to infect. One of these, NEF (which is a key part in the development of AIDS) helps the process by blocking the SERINC proteins, so that they are unable to reach the cell’s surface. This means that they will no longer become a part of the newly formed virions. Developing a drug to restrict NEFs would allow the system to fight HIV, as the virions would then include SERINC3 and SERINC5 making them unable to infect new cells. This process could then be applied to other infectious viruses with NEF proteins.
The researchers found that there are proteins in the T-cells in our immune system which naturally fight HIV. SERINC5 and SERINC3, two host cell proteins, are able to stifle HIV-1 by greater than 100-fold. The HIV-1 genome has nine genes which can be replicated in the host cell, which then produce virions (the infectious part of the virus). They begin a cycle of infection by looking for new cells to infect. One of these, NEF (which is a key part in the development of AIDS) helps the process by blocking the SERINC proteins, so that they are unable to reach the cell’s surface. This means that they will no longer become a part of the newly formed virions. Developing a drug to restrict NEFs would allow the system to fight HIV, as the virions would then include SERINC3 and SERINC5 making them unable to infect new cells. This process could then be applied to other infectious viruses with NEF proteins.

 The team were able to identify three proteins that are responsible for stopping NPQ. They speculated that plants with increased numbers of these proteins would be able to relax the process faster. The theory was tested using tobacco, because of the ease with which these plants are transformed and their ability to produce the layers of leaves necessary. Those that had additional proteins added weighed between 14% and 20% more than other tobacco plants. Many crops such as rice, soybeans and wheat, also produce layers. This suggests that the same method can be applied to these foods, increasing their yield. Even though the crops would be more difficult to modify, researchers are confident that this next step in the experiment can be achieved fairly quickly.
The team were able to identify three proteins that are responsible for stopping NPQ. They speculated that plants with increased numbers of these proteins would be able to relax the process faster. The theory was tested using tobacco, because of the ease with which these plants are transformed and their ability to produce the layers of leaves necessary. Those that had additional proteins added weighed between 14% and 20% more than other tobacco plants. Many crops such as rice, soybeans and wheat, also produce layers. This suggests that the same method can be applied to these foods, increasing their yield. Even though the crops would be more difficult to modify, researchers are confident that this next step in the experiment can be achieved fairly quickly.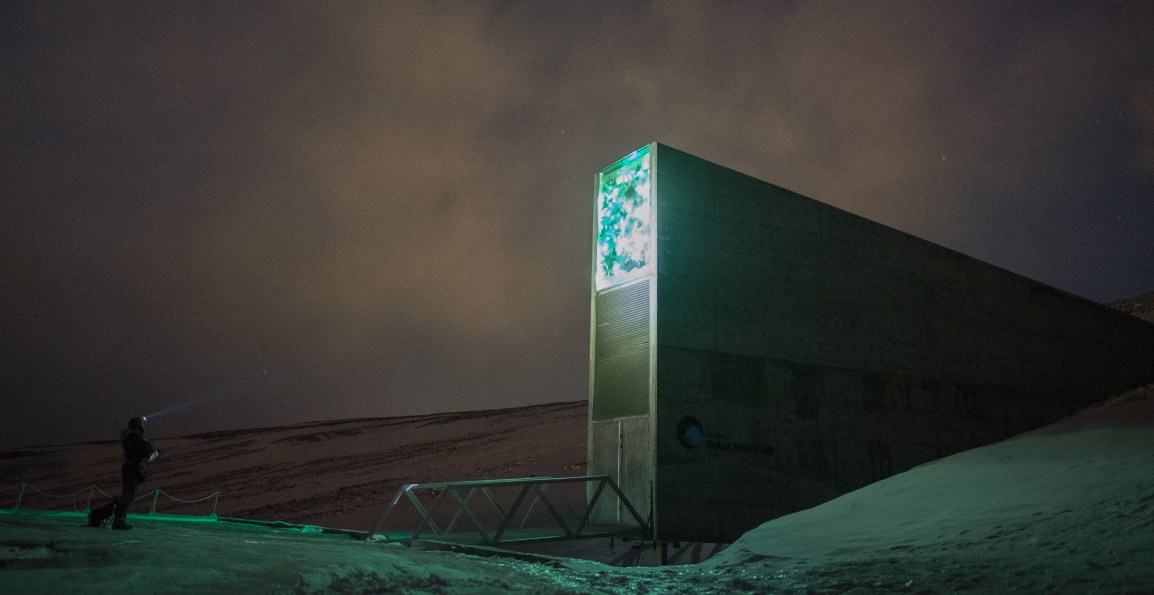
 The site for the seed bank was chosen for a number of reasons, including the fact there the area has a minimal amount of tectonic activity. It is also surrounded by permafrost, which will aid in the preservation of the seeds. Another major factor was its height, 130m above sea level, which would allow the vault to remain dry in the event of the surrounding ice caps melting. This was not expected to take place for at least several decades, however. Unfortunately, with global warming accelerating at an alarming rate, the vault’s capabilities have already been put to the test.
The site for the seed bank was chosen for a number of reasons, including the fact there the area has a minimal amount of tectonic activity. It is also surrounded by permafrost, which will aid in the preservation of the seeds. Another major factor was its height, 130m above sea level, which would allow the vault to remain dry in the event of the surrounding ice caps melting. This was not expected to take place for at least several decades, however. Unfortunately, with global warming accelerating at an alarming rate, the vault’s capabilities have already been put to the test. The area surrounding the vault is currently one of the most susceptible to the dangers of global warming, as the temperatures in the Arctic rise quicker than the rest of the world. These dangers are increasing at an alarming rate, with 2016 being the hottest year to date and 2017 expected to surpass it. Even though the vault’s structure has proven to be safe for the seeds’ preservation, Norway is making improvements to the surrounding area to ensure that any water surrounding it will drain away properly. They have emphasized that these seeds are being preserved to benefit the entire world, and need to be protected at all costs. The country has also emphasized the need for worldwide changes to minimize the drastic acceleration of global warming.
The area surrounding the vault is currently one of the most susceptible to the dangers of global warming, as the temperatures in the Arctic rise quicker than the rest of the world. These dangers are increasing at an alarming rate, with 2016 being the hottest year to date and 2017 expected to surpass it. Even though the vault’s structure has proven to be safe for the seeds’ preservation, Norway is making improvements to the surrounding area to ensure that any water surrounding it will drain away properly. They have emphasized that these seeds are being preserved to benefit the entire world, and need to be protected at all costs. The country has also emphasized the need for worldwide changes to minimize the drastic acceleration of global warming.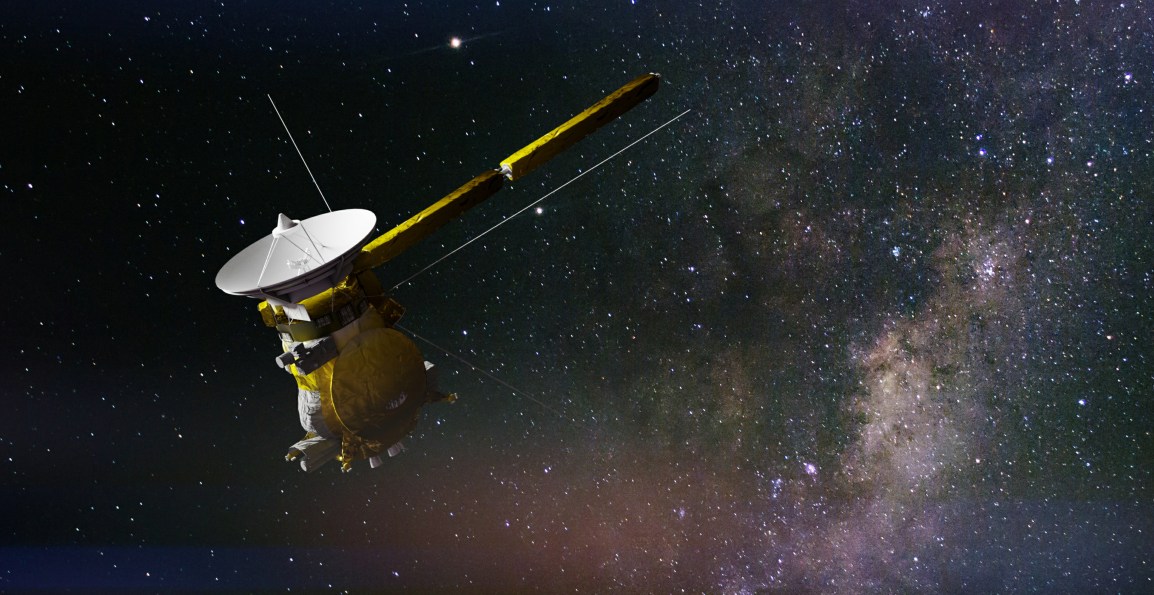
 end with ‘The Grand Finale.’ This event is scheduled to incorporate 22 deep dives between the planet’s clouds and innermost ring, ending with a massive plunge directly into its atmosphere.
end with ‘The Grand Finale.’ This event is scheduled to incorporate 22 deep dives between the planet’s clouds and innermost ring, ending with a massive plunge directly into its atmosphere.


