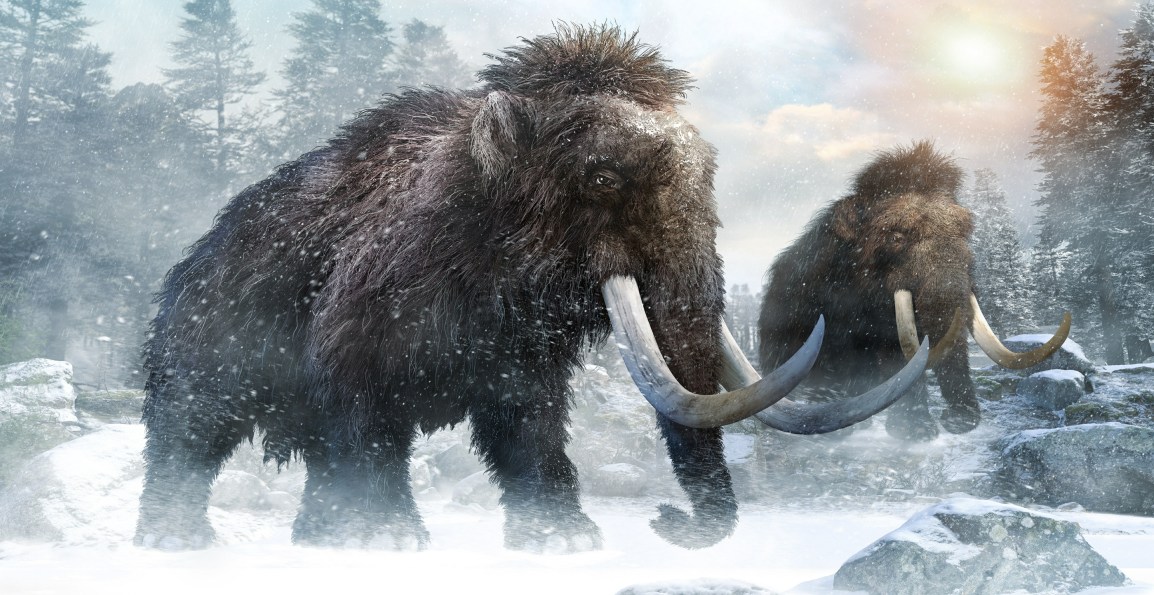
Ever thought the giant sized tusked wooly elephants who went extinct some 10,000 years ago and only recently seen in animated movies & ancient history programs will come to life on this earth again? That’s exactly what US based startup Colossal Biosciences has announced and already secured funding of $15 million.
The project spearheaded by Harvard geneticist George Church aims to use CRISPR gene editing technology to engineer Asian elephant embryos with characteristics closest to the now extinct Wooly Mammoths. The idea is to create and then release these giants in the Arctic Tundra region in a bid to positively impact the ecosystem and play their role in environmental conservation. The scientists at Colossal Biosciences also believe that if they are successful in recreating the Wooly Mammoths, they might even be able to prevent the extinction of other endangered species.

Possible Hurdles that Scientists Face in Reengineering Mammoths
While it all sounds pretty fascinating, the whole idea or reintroducing the Wooly Mammoths into the wild will need a lot of thinking. There’s a lot that needs to be addressed before the scientists in George Church’s team attempt to recreate the giants. For instance, scientists are already questioning how will these giant Mammoths be gestated? While there is no mature technology for artificial wombs which could be used to gestate the Mammoth embryos, scientists around the world are quite skeptical about using an Asian elephant as the mother, which are listed as endangered species themselves.
Also, it must be considered that the present day human race knows very little about the Wooly Mammoths. With such little knowledge, releasing these giants into the Arctic Tundra is another point of concern.
Real Mammoths or Hybrids
Another big question being raised by scientists is that whether or not these Wooly Mammoths will be what Colossal Biosciences claims them to be. Asian elephants generally share 99% of their DNA with this particular mammoth species but with smaller ears and a stark shaggy coat, this animal will most likely be an elephant-mammoth hybrid and not the real ancient mammoths.

While researchers have previously discovered calves of wooly mammoths in the permafrost, scientists at Colossal Biosciences agree that it might be really hard to study the properties of the mammoth and that it is highly likely this project might very well be impossible to successfully complete.
What Does this Mean for Biosciences?
Church’s cofounder at Colossal, software entrepreneur Ben Lamm, said “I hope the tech could prevent the extinction of endangered mammals like elephants and rhinoceroses, or even let conservationists tinker with the genetic code of existing creatures to help them survive a changing climate.”
“We can leverage these genetic tools,” he further said, to “allow for species to not be isolated to one geographic location, but be adaptable to others.”