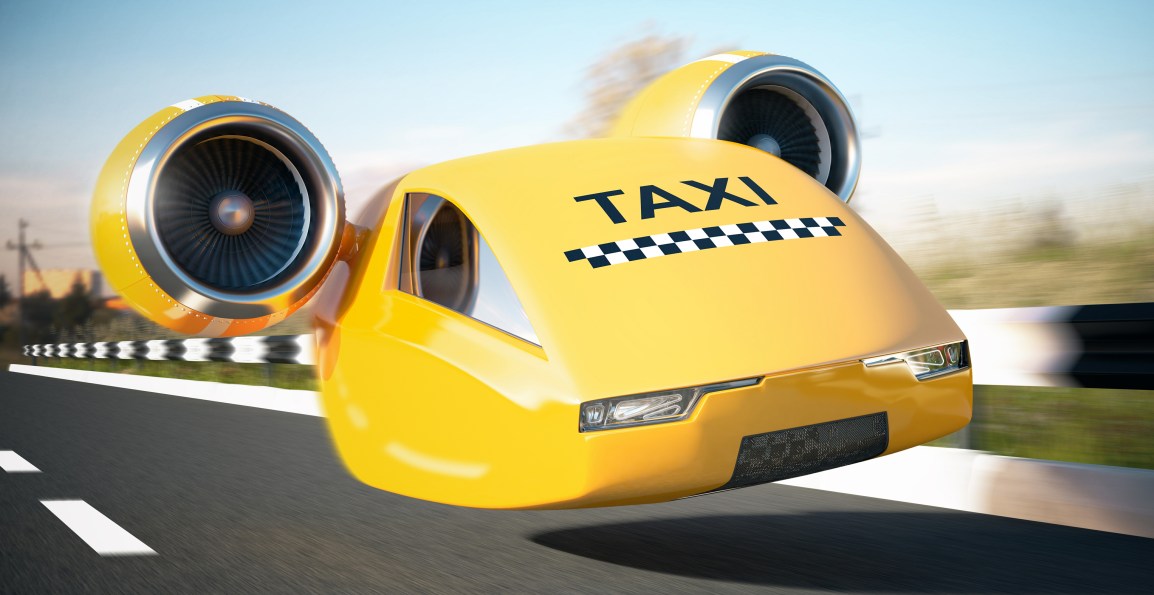
Futuristic movies and books have featured flying vehicles for many years, and technology has finally caught up with the human imagination. Companies are now designing cars that will take to the skies to provide us with commuting options. In February 2016, Airbus advanced on a project with a mission to solve the ever increasing traffic in urban areas. They aim to do this by creating the world’s first approved ‘air taxi,’ which will operate on a system similar to ordering an Uber, using a smartphone.
 Project Vahana, as the undertaking has been named, currently faces many challenges. These include air traffic management hurdles, as well as structural requirements for such a vehicle. Spokespersons for Airbus have said that their aim is to work with several other companies in order to overcome these obstacles. They have already begun to take into consideration the regulations that the Federal Aviation Administration will be putting into place, in order to approve the use of flying vehicles.
Project Vahana, as the undertaking has been named, currently faces many challenges. These include air traffic management hurdles, as well as structural requirements for such a vehicle. Spokespersons for Airbus have said that their aim is to work with several other companies in order to overcome these obstacles. They have already begun to take into consideration the regulations that the Federal Aviation Administration will be putting into place, in order to approve the use of flying vehicles.
With urban congestion predicted to increase by at least 10% by 2030, the company believe that millions of their innovative cars will be needed worldwide as a result. They have already designed and begun to build their first prototype. This VTOL (Vertical Take Off and Landing) will operate similarly to a helicopter. Even though it will be equipped with self-piloting technology, the vehicle will be introduced with human behind the wheel, until the approval to have autonomous flight has been granted. Sense-and-avoid technology is relatively new in vehicles, and needs to be further tested in those that are airborne before they can be declared safe for public use. Currently drones, even though able to fly themselves, are not allowed to be in open air space without being monitored remotely by a human and the technology used to power larger vehicles is very similar.
 In addition to the pilot, the expectation is that the vehicle will at first be able to carry a single passenger. A testing contract has been granted to the company and they have chosen to have their first trial flights in Singapore. Airbus has said that their aim is to begin testing their prototype by the end of 2017. They are well on their way to meeting this target, after which they plan to introduce the vehicles to commuters by 2020. They are confident that this will be the biggest solution to the current traffic problem that the world is experiencing.
In addition to the pilot, the expectation is that the vehicle will at first be able to carry a single passenger. A testing contract has been granted to the company and they have chosen to have their first trial flights in Singapore. Airbus has said that their aim is to begin testing their prototype by the end of 2017. They are well on their way to meeting this target, after which they plan to introduce the vehicles to commuters by 2020. They are confident that this will be the biggest solution to the current traffic problem that the world is experiencing.
Airbus is not the only company with this futuristic ambition, however, and their competitors are already working on similar designs. Google and Uber are just two of the others that have announced plans to release air commuting vehicles. Regardless of which company is able to release their design first, the only thing we can be sure of is that the future has already become the present.


 The unit is made from a special type of material, designed by the company, which is able to absorb water from the air. Its solar panels are then able to harvest the energy from the sun to heat the liquid enough to turn it into steam. This evaporation is the way in which the water is purified. It is then run through a mineral block, adding beneficial nutrients and improving the taste.
The unit is made from a special type of material, designed by the company, which is able to absorb water from the air. Its solar panels are then able to harvest the energy from the sun to heat the liquid enough to turn it into steam. This evaporation is the way in which the water is purified. It is then run through a mineral block, adding beneficial nutrients and improving the taste.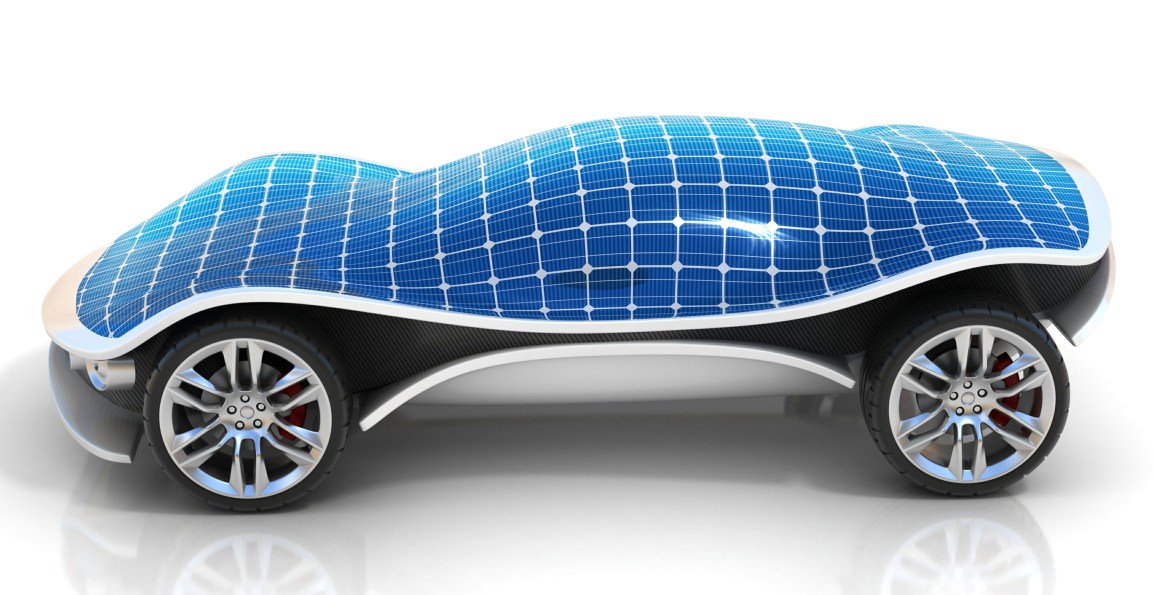
 The increase in making renewable energy vehicles would mean a decline in the labor force, within automobile companies, as they require less manpower to produce. The country is prepared to deal with this unemployment in different ways, as they have decided that the pros greatly outnumber the cons. In addition to directly impacting global warming and keeping the climate under control, using renewable energy in cars would mean healthier citizens, as well as overall economic benefits, due to the fact that they cost less to make and operate.
The increase in making renewable energy vehicles would mean a decline in the labor force, within automobile companies, as they require less manpower to produce. The country is prepared to deal with this unemployment in different ways, as they have decided that the pros greatly outnumber the cons. In addition to directly impacting global warming and keeping the climate under control, using renewable energy in cars would mean healthier citizens, as well as overall economic benefits, due to the fact that they cost less to make and operate.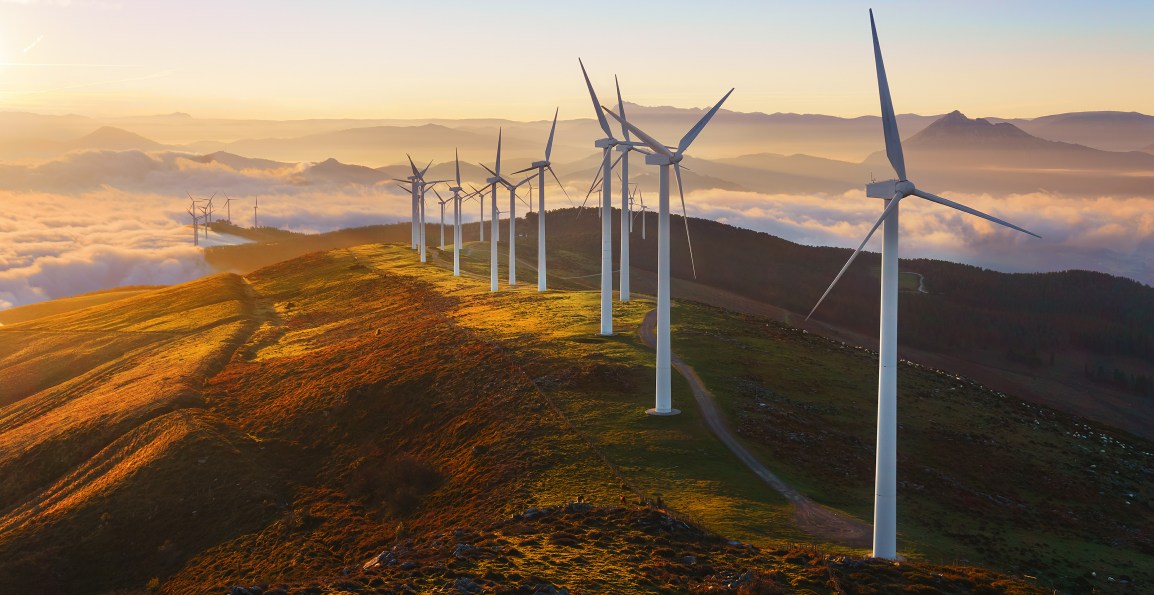
 During the Yokohama Renewable Energy International Exhibition 2010, they unveiled the new design, which works by putting a wind lens around the turbine blades. This also makes it possible to increase their safety levels, as well as decrease the unbearable noise usually associated with wind turbines. The wind lens is a brim that surrounds the inside of the blades and diverts the air from the exhaust outflow, which is located behind them. The turbulence then creates a low pressure zone behind the turbine, which causes more wind to pass through it. The blade rotation increases and subsequently the energy output. The engineers believe that each lens would be able to provide enough energy for an average household.
During the Yokohama Renewable Energy International Exhibition 2010, they unveiled the new design, which works by putting a wind lens around the turbine blades. This also makes it possible to increase their safety levels, as well as decrease the unbearable noise usually associated with wind turbines. The wind lens is a brim that surrounds the inside of the blades and diverts the air from the exhaust outflow, which is located behind them. The turbulence then creates a low pressure zone behind the turbine, which causes more wind to pass through it. The blade rotation increases and subsequently the energy output. The engineers believe that each lens would be able to provide enough energy for an average household. These wind turbines are being monitored as part of their larger project to build an offshore energy farm. The wind turbines will be mounted on a hexagonal shaped base, which is low in cost but sufficiently sturdy to withstand the marine conditions. Placing these in coastal areas will take advantage of the sea breezes, and reveal the probability of them being a main source of power for the country. The bases also make it possible to link other turbines together and create larger platforms.
These wind turbines are being monitored as part of their larger project to build an offshore energy farm. The wind turbines will be mounted on a hexagonal shaped base, which is low in cost but sufficiently sturdy to withstand the marine conditions. Placing these in coastal areas will take advantage of the sea breezes, and reveal the probability of them being a main source of power for the country. The bases also make it possible to link other turbines together and create larger platforms.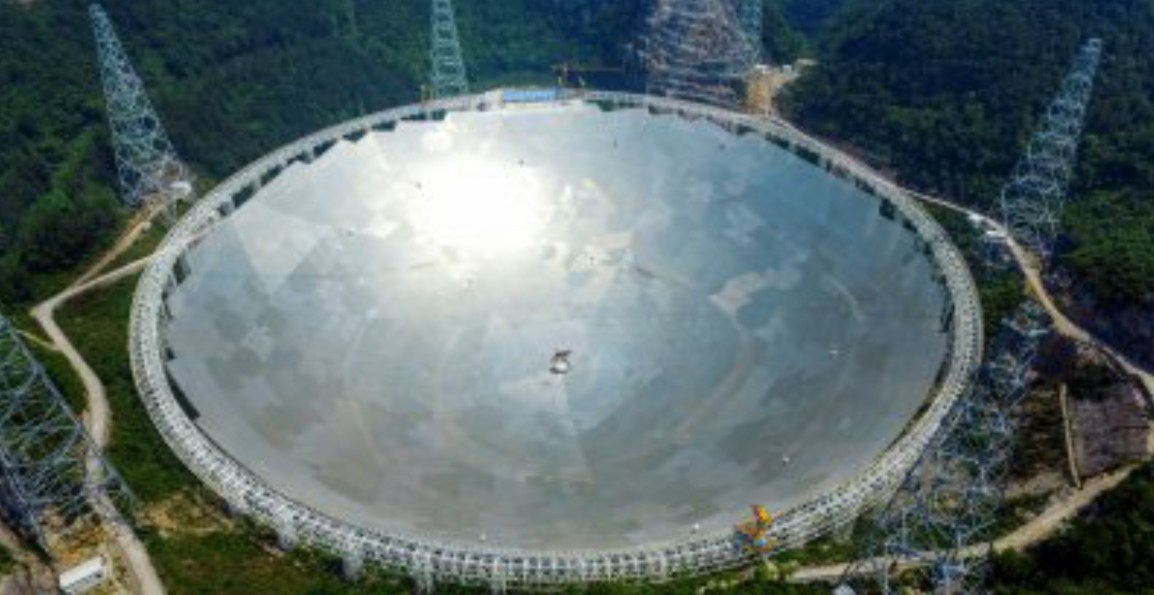
 Many of the countries of the world are experimenting with different ways to find out more about the Universe, especially the possibility of finding intelligent life outside of our planet. China has been a large contributor to this extra-terrestrial search, and the country has recently unveiled their next step in learning more about the infinite nature of the Universe. They have done this by launching a 500m Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), which has now become the largest in the world. Approximately the size of 30 football fields, FAST took five years to be built and launched. The single dish telescope has been nicknamed the Tianyan, or Eye of Heaven, because it is expected to be able to capture a great deal more of what happens outside of our atmosphere than we have previously been aware of.
Many of the countries of the world are experimenting with different ways to find out more about the Universe, especially the possibility of finding intelligent life outside of our planet. China has been a large contributor to this extra-terrestrial search, and the country has recently unveiled their next step in learning more about the infinite nature of the Universe. They have done this by launching a 500m Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), which has now become the largest in the world. Approximately the size of 30 football fields, FAST took five years to be built and launched. The single dish telescope has been nicknamed the Tianyan, or Eye of Heaven, because it is expected to be able to capture a great deal more of what happens outside of our atmosphere than we have previously been aware of.
 1. Uber
1. Uber 2. Nutonomy
2. Nutonomy