The global temperature has been rising at a disturbing rate in recent decades. This incline has partially been attributed to the burning of fossil fuels in different forms. In December 2015, 195 countries collaborated to take action against climate change, by signing a legally, binding agreement called The Paris Agreement. This agreement will take effect in 2020 and aims to avoid many detrimental effects of a higher global temperature. The main requirement is to limit the rise in global temperature to 2°C. Many of the countries involved are already putting necessary procedures into effect in order to do so.
Germany has the fourth largest output of automobiles in the world, and its government has made a proposal to ban internal combustion engines by 2030. This would mean that no new cars will require any type of fuel or diesel to operate. The majority of the vehicles in operation would then run exclusively on renewable energy. They have also suggested that the tax subsidies that are given to diesel automobile makers be lowered, in an effort to bring this change into effect sooner rather than later.
 The increase in making renewable energy vehicles would mean a decline in the labor force, within automobile companies, as they require less manpower to produce. The country is prepared to deal with this unemployment in different ways, as they have decided that the pros greatly outnumber the cons. In addition to directly impacting global warming and keeping the climate under control, using renewable energy in cars would mean healthier citizens, as well as overall economic benefits, due to the fact that they cost less to make and operate.
The increase in making renewable energy vehicles would mean a decline in the labor force, within automobile companies, as they require less manpower to produce. The country is prepared to deal with this unemployment in different ways, as they have decided that the pros greatly outnumber the cons. In addition to directly impacting global warming and keeping the climate under control, using renewable energy in cars would mean healthier citizens, as well as overall economic benefits, due to the fact that they cost less to make and operate.
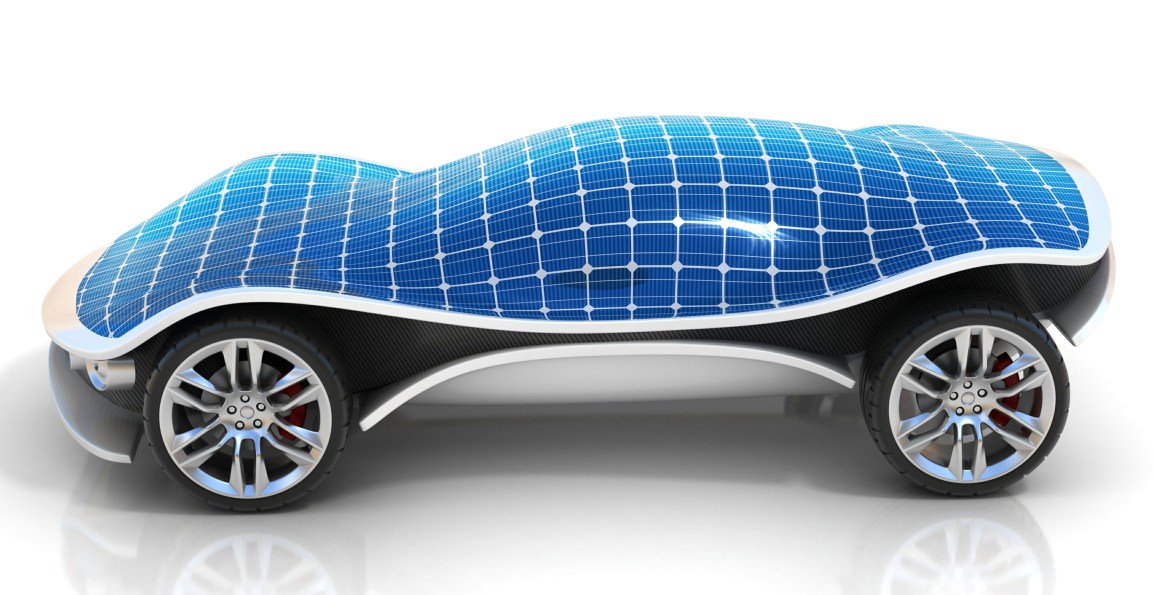
The energy sources that environmentally friendly vehicles are able to run on currently include plug-in hybrids, fuel cell powered hydrogen cars and chargeable electric cars. There are also companies creating vehicular prototypes which operate on solar and wind energy. As the largest source of renewable energy, many are hoping to use the sun to power vehicles in two separate ways. The first would be to install solar panels on the roofs of cars, and the second would be to have chargers for cars which are fed by solar powered generators. There are prototypes of both currently being monitored and revised.
Large car manufacturers have seen the value in producing renewable energy vehicles and companies such as BMW, Ford and Toyota already sell hybrids which use various forms of cleaner energy. Volkswagen has set a goal to become the largest automaker in the world, and believes that renewable energy will be one of the best ways to do so. A huge percentage of their funds are put towards researching the best ways of powering these vehicles in the future.
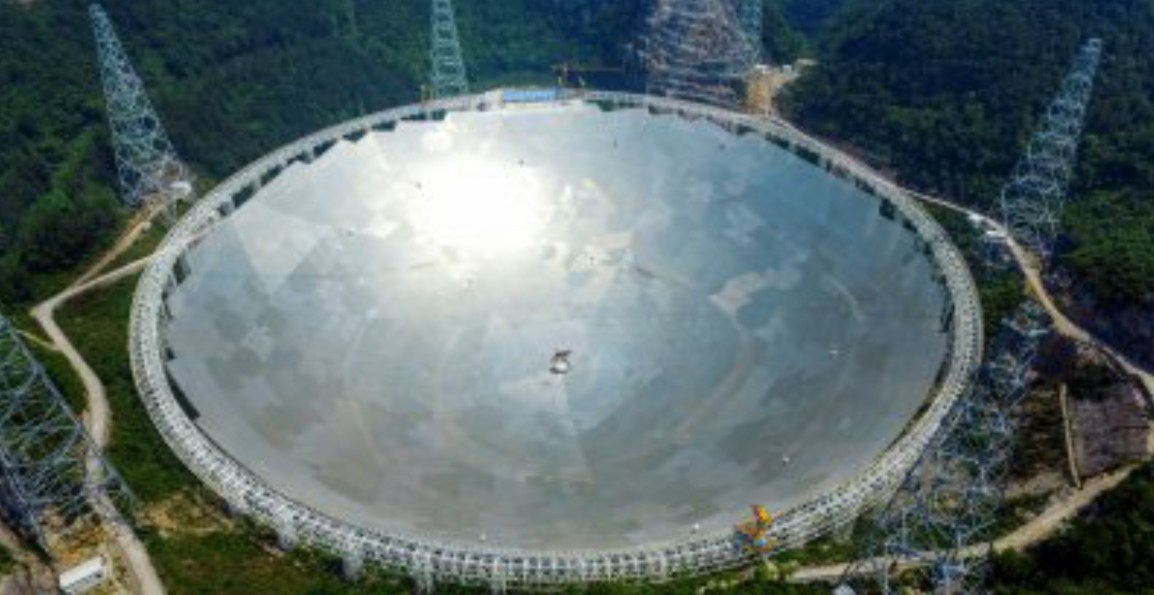

 Many of the countries of the world are experimenting with different ways to find out more about the Universe, especially the possibility of finding intelligent life outside of our planet. China has been a large contributor to this extra-terrestrial search, and the country has recently unveiled their next step in learning more about the infinite nature of the Universe. They have done this by launching a 500m Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), which has now become the largest in the world. Approximately the size of 30 football fields, FAST took five years to be built and launched. The single dish telescope has been nicknamed the Tianyan, or Eye of Heaven, because it is expected to be able to capture a great deal more of what happens outside of our atmosphere than we have previously been aware of.
Many of the countries of the world are experimenting with different ways to find out more about the Universe, especially the possibility of finding intelligent life outside of our planet. China has been a large contributor to this extra-terrestrial search, and the country has recently unveiled their next step in learning more about the infinite nature of the Universe. They have done this by launching a 500m Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), which has now become the largest in the world. Approximately the size of 30 football fields, FAST took five years to be built and launched. The single dish telescope has been nicknamed the Tianyan, or Eye of Heaven, because it is expected to be able to capture a great deal more of what happens outside of our atmosphere than we have previously been aware of.
 1. Uber
1. Uber 2. Nutonomy
2. Nutonomy
 Amazon’s Delivery Drone
Amazon’s Delivery Drone 
 The possibilities of space exploration would become unlimited with the use of the EM drive, which would be able to transport humans to Mars in 70 days (presently it takes between 150 and 300). It is rumoured that the years of research into the possibility of sending one into space has now been peer approved, and papers regarding the device are expected to be published shortly. In addition, Guida Fetta has designed a rocket engine based on the original concept of Shawyer’s EM drive and plans to launch it on a miniature satellite within a few months. His team of scientists will let it remain in orbit for at least six months to prove that the drive will continue to work over an extended period of time.
The possibilities of space exploration would become unlimited with the use of the EM drive, which would be able to transport humans to Mars in 70 days (presently it takes between 150 and 300). It is rumoured that the years of research into the possibility of sending one into space has now been peer approved, and papers regarding the device are expected to be published shortly. In addition, Guida Fetta has designed a rocket engine based on the original concept of Shawyer’s EM drive and plans to launch it on a miniature satellite within a few months. His team of scientists will let it remain in orbit for at least six months to prove that the drive will continue to work over an extended period of time.