The use of robots in their production line has been proving to be remarkably profitable for many businesses. One of the reasons for this is because it immediately decreases one of their largest regular pay-outs, labor costs. This means that factories, and other businesses with many employees, have increased their use of automation by adding robots to their labor force. The machines have also proven to be significantly more efficient than human labor. Instrumental in this change are many Chinese companies, which are responsible for a large part of the world’s production. As a result, they have been investing significantly in finding mechanical forces that will decrease the cost of labor, as well as continue to boost productivity levels.
Shentong Express, a large-scale shipping company, has cut its labor costs in half by making sorting robots a permanent part of its labor force. The robots are made by Hikvision, and are responsible for sorting parcels as they transition through the system. Each machine can sort at least 200,000 parcels per day and, since they are self-charging, can work around the clock. This has also facilitated an improvement in the company’s efficiency by 30%, as well as increasing the accuracy of sorting. Even though the robots are currently only a part of the work force in two of the company’s Hangzhou branches, there are plans to expand their use to all their largest branches.
In 2016, the output using industrial robots increased by over 30%, fuelling the shift from human work forces to automated ones. Another Chinese company, Changying Precision Technology, which manufactures mobile phones, automated 90% of their work force. This meant that 650 human workers were replaced with 60 robots, across 10 production lines. The company’s productivity has subsequently increased by 250%, and defective products decreased by 80%. These results have caused China to develop a long-term plan which involves using robots as a significant part of their labor force, increasing their number to 100,000 by 2020.
Even though large-scale businesses embrace these changes, many individuals are worried about the considerable number of people that will lose their jobs due to increased levels of automation and technological advancements. It is estimated that within the next 20 years, 137 million workers in five Southeast Asian countries will be replaced with robots or other automated systems.
There are other changes that automation will bring to business worldwide. Many companies in first world countries have previously outsourced their production, to others that are less developed with low cost labor forces. Automation means that production can be transferred to the home country, since labor costs would now be at a minimum. This would have detrimental effect on the economy of many third world countries.
Internationally, the use of automated services must be embraced, without taking things to the extreme. Viable solutions will also need to be found to control the expected rise in the unemployment rate. One suggestion is to have a universal basic income, which would expand economies and limit unemployment.



 Previously unused technology has been applied to the vehicle’s design and manufacturing process, but Musk says consumers are unlikely to notice the changes. In 2014, Tesla introduced their semi-autonomous driving system, Autopilot, which will also be included in the Model 3’s features. Self-driving vehicles increase road safety, and Tesla has plans to include this it in all their productions. Due to its Autopilot capabilities, the Model 3 will be equipped with a single dashboard, since the driver will need to view less information.
Previously unused technology has been applied to the vehicle’s design and manufacturing process, but Musk says consumers are unlikely to notice the changes. In 2014, Tesla introduced their semi-autonomous driving system, Autopilot, which will also be included in the Model 3’s features. Self-driving vehicles increase road safety, and Tesla has plans to include this it in all their productions. Due to its Autopilot capabilities, the Model 3 will be equipped with a single dashboard, since the driver will need to view less information.
 A team of researchers from the University of California, have recently developed a drug which can restore insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes. It would be administered via a single pill taken daily, and works by inhibiting LMPTP (low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase) which contributes to the reduction in cell sensitivity to insulin. Decreasing the amount of the enzyme in the body, causes the cells (especially those in the liver), to become receptive to insulin once again. This then restores the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, ultimately reversing the condition.
A team of researchers from the University of California, have recently developed a drug which can restore insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes. It would be administered via a single pill taken daily, and works by inhibiting LMPTP (low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase) which contributes to the reduction in cell sensitivity to insulin. Decreasing the amount of the enzyme in the body, causes the cells (especially those in the liver), to become receptive to insulin once again. This then restores the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, ultimately reversing the condition. The concept of reversing diabetes is not a new one, and has previously been achieved using a combination of drugs, a strict diet and a regular exercise regime. Scientists at Cornell University have also found that probiotic pills, containing live bacteria, can help reverse the effects of Type 2 diabetes by ‘rewiring’ the body. The probiotic pill was also tested on rodents, and managed to shift the control of the body’s blood sugar levels from the pancreas (which normally controls glucose levels within the body) to the upper intestine. By shifting where the blood sugar levels are controlled, scientists found that the animals’ insulin levels increased by up to 30%. They believe that a higher dose of this probiotic pill may become a cure for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
The concept of reversing diabetes is not a new one, and has previously been achieved using a combination of drugs, a strict diet and a regular exercise regime. Scientists at Cornell University have also found that probiotic pills, containing live bacteria, can help reverse the effects of Type 2 diabetes by ‘rewiring’ the body. The probiotic pill was also tested on rodents, and managed to shift the control of the body’s blood sugar levels from the pancreas (which normally controls glucose levels within the body) to the upper intestine. By shifting where the blood sugar levels are controlled, scientists found that the animals’ insulin levels increased by up to 30%. They believe that a higher dose of this probiotic pill may become a cure for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.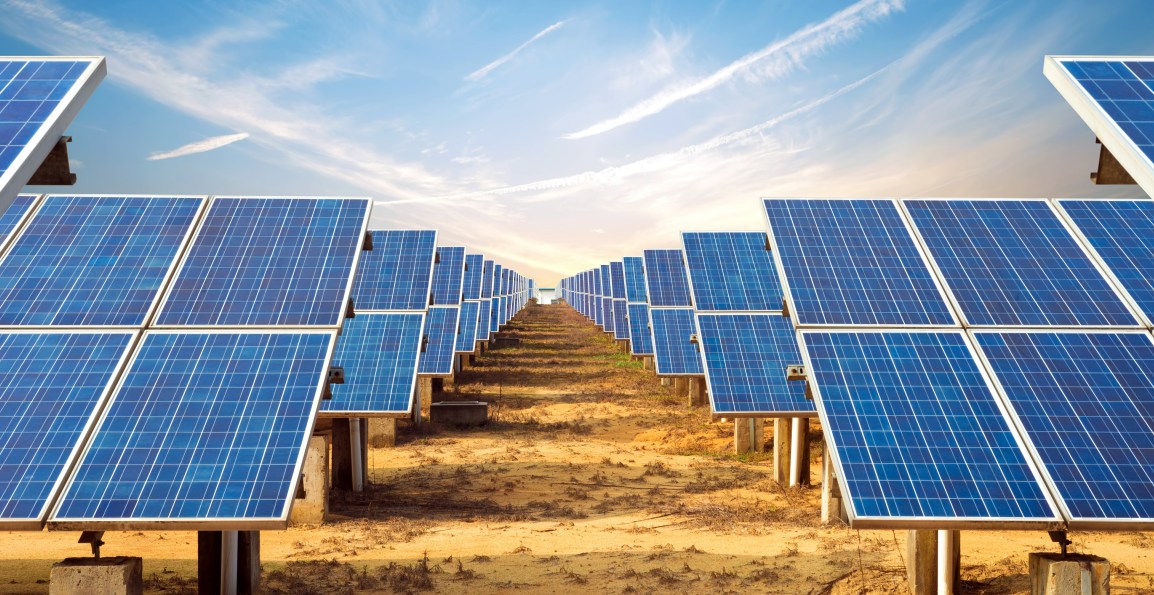
 The World Economic Forum (WEF) has also published a report, stating that renewable energy sources have become more efficient. It states that many of them are now able to compete with the price of fossil fuels, and are even cheaper in many cases. Large companies, as well as entire countries, have begun investing in wind and solar technology. Infrastructure for major organisations and projects now includes solar panels, that have been installed to save on energy costs.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) has also published a report, stating that renewable energy sources have become more efficient. It states that many of them are now able to compete with the price of fossil fuels, and are even cheaper in many cases. Large companies, as well as entire countries, have begun investing in wind and solar technology. Infrastructure for major organisations and projects now includes solar panels, that have been installed to save on energy costs. With increased use of renewable energy being a part of the global plan to monitor climate change, governments are doing their part in making these changes. Many countries are working with car manufacturers to create a transportation system that lowers the use of vehicles that burn fuel. The manufacturers are making more electric vehicles, and governments have approved the installation of more charging stations. In addition to this, solar panels are also being provided at lower costs for use in homes, and many new buildings come with them pre-installed.
With increased use of renewable energy being a part of the global plan to monitor climate change, governments are doing their part in making these changes. Many countries are working with car manufacturers to create a transportation system that lowers the use of vehicles that burn fuel. The manufacturers are making more electric vehicles, and governments have approved the installation of more charging stations. In addition to this, solar panels are also being provided at lower costs for use in homes, and many new buildings come with them pre-installed.


 The telescope had been created by the combined expertise of NASA, The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The object is scheduled to be launched into outer space, on an ESA Ariane V Booster from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana in 2018. Previously, telescopes that were launched into space relied on rigid structures for their stability. The Webb is the first of its kind to be built for both stability and mobility. Its honeycomb appearance is because of its 18-segment ‘golden’ primary mirror, which will need to be folded to fit inside its carrier. When the launch is complete and the telescope safely in space, the mirror will unfold to begin its observations.
The telescope had been created by the combined expertise of NASA, The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The object is scheduled to be launched into outer space, on an ESA Ariane V Booster from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana in 2018. Previously, telescopes that were launched into space relied on rigid structures for their stability. The Webb is the first of its kind to be built for both stability and mobility. Its honeycomb appearance is because of its 18-segment ‘golden’ primary mirror, which will need to be folded to fit inside its carrier. When the launch is complete and the telescope safely in space, the mirror will unfold to begin its observations.