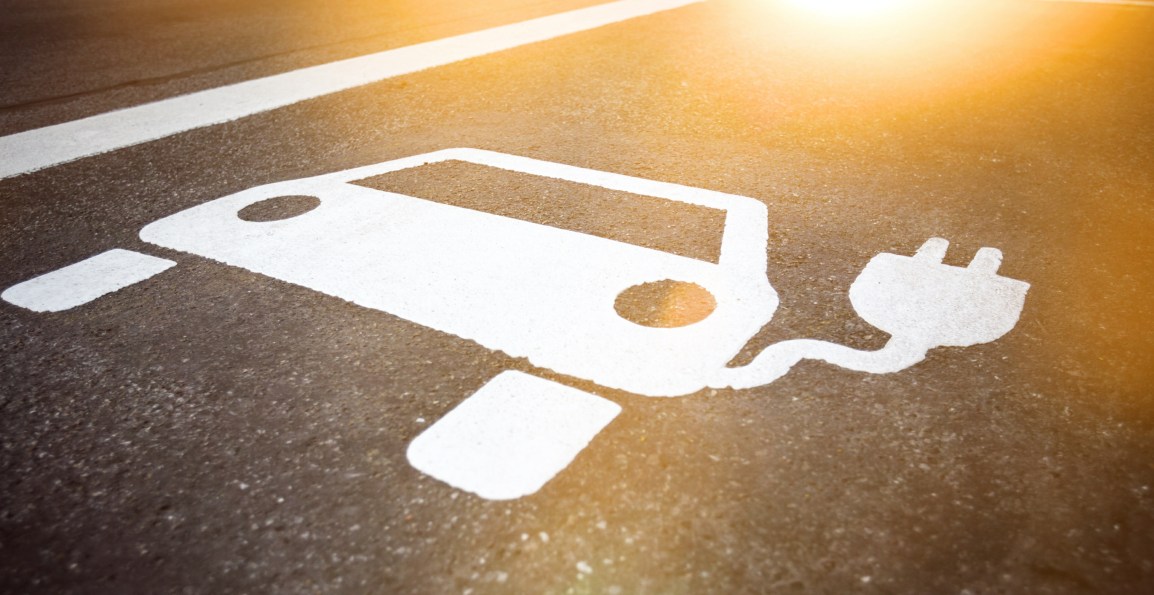
The number of electric vehicles on the road has increased exponentially over the last few years. This is mainly a result of environmental concerns and governments becoming more focused on finding sustainable energy sources. Sweden has recently become the first country to install a section of the road that can recharge the batteries of vehicles as they drive along it. The project consisted of embedding 2 km of electric rail, in a location near Stockholm, and is in accordance with the country’s plans to stop using vehicles that run on  fossil fuels by 2030. The government has already drafted a map to install more electric charging roads to keep the batteries of electric vehicles affordable, as well as to prevent them from losing their charge during a journey.
fossil fuels by 2030. The government has already drafted a map to install more electric charging roads to keep the batteries of electric vehicles affordable, as well as to prevent them from losing their charge during a journey.
The length of the road extends from Stockholm Arlanda Airport to a logistics site outside the capital city. Vehicles can be charged by energy being transferred from two tracks of rail in the road, using a movable arm attached to their undercarriage. This would be automatically disconnected if a vehicle stops or is overtaking another one. The electric charging road is currently divided into sections of 50m, each of which is only powered on when a vehicle is directly overhead. Citizens that take advantage of the service will be billed based on the energy consumption of their vehicle. The first vehicle to use Sweden’s ‘dynamic charging’ facilities was a truck owned by logistics firm, PostNord, which previously ran on diesel.
eRoadArlanda oversaw the project’s completion and has ensured the public that the country’s roads, as well as the vehicles currently being driven on them, could be adapted to take advantage of the technology. Sweden plans to install the technology in the 20,000km of highways that the country has. This would provide enough power to recharge any vehicle traveling in the country, as the longest distance between highways is 45km and all electric vehicles can travel that far without the need to recharge. Each km of the electric road cost U$1.2 million to install, but the government has estimated this to be 50 times less than the installation of a tram line. They also guarantee the roads’ safety, as the electricity is located five or six centimeters below the surface.
In addition to expanding within their own country, the Swedish government is making plans to provide Berlin with a similar network in the future. Other countries have already made the investment for public vehicles, including Israel which has installed roads to power their electric buses. The technology would currently not be applicable to most countries, due to the condition that many of the roads are in and the unlikely need for most vehicles to recharge during their journey. The inflated cost of installing these roads is also a deterrent. For Sweden and heavy-duty vehicles, such as the PostNord truck, EV charging roads are an ideal, convenient solution, however.



 MIT has collaborated with a new company, Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS), in the hopes of bringing the world’s first successful fusion power plant to working order within the next 15 years. The collaboration is using a unique form of production, called SPARC, which will build smaller, more powerful field magnets using new high-temperature superconductors. The material that will be used in their creation has recently been introduced to the market, and will result in the magnets being four times stronger than any previously used in fusion experiments. Development time for these has been estimated to be within the next three years.
MIT has collaborated with a new company, Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS), in the hopes of bringing the world’s first successful fusion power plant to working order within the next 15 years. The collaboration is using a unique form of production, called SPARC, which will build smaller, more powerful field magnets using new high-temperature superconductors. The material that will be used in their creation has recently been introduced to the market, and will result in the magnets being four times stronger than any previously used in fusion experiments. Development time for these has been estimated to be within the next three years.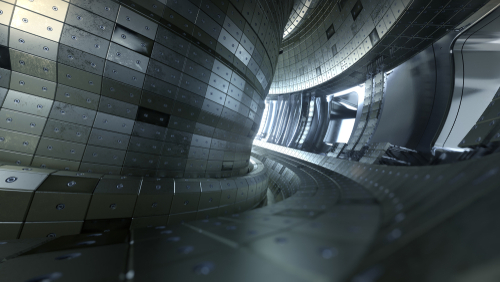 magnets would result in fusion power being used as an alternative energy source, helping to decrease climate change due to its lack of emissions.
magnets would result in fusion power being used as an alternative energy source, helping to decrease climate change due to its lack of emissions.
 website-publishing technology that will be available for all site owners to take advantage of. It will allow them to increase the speed of their pages, without losing the value of having ads on their website.
website-publishing technology that will be available for all site owners to take advantage of. It will allow them to increase the speed of their pages, without losing the value of having ads on their website.

 SpaceX, one of his companies with a shaky past, has surpassed expectations with its recent achievements. In February it achieved a successful launch of Falcon Heavy, and Musk said that their new aim was to complete the BFR in the shortest amount of time possible. The goal is for this rocket to be the first to transport humanity to Mars, which Musk believes is essential to the survival of our species. He declared that test flights are expected in 2019, even though he did acknowledge that his enthusiasm does sometimes result in unrealistic deadlines. In addition to the test next year, SpaceX is expected to conduct their first cargo journey to Mars in 2022, with crewed missions following by 2024.
SpaceX, one of his companies with a shaky past, has surpassed expectations with its recent achievements. In February it achieved a successful launch of Falcon Heavy, and Musk said that their new aim was to complete the BFR in the shortest amount of time possible. The goal is for this rocket to be the first to transport humanity to Mars, which Musk believes is essential to the survival of our species. He declared that test flights are expected in 2019, even though he did acknowledge that his enthusiasm does sometimes result in unrealistic deadlines. In addition to the test next year, SpaceX is expected to conduct their first cargo journey to Mars in 2022, with crewed missions following by 2024. development of artificial intelligence. This led him to stress the importance of developing AI safely, a field in which he is ‘very close to the cutting edge.’ It was apparent in his manner, however, that this concept both fascinated and terrified him simultaneously. In Musk’s own words, ‘AI is much more dangerous than nukes,’ and requires a ‘regulatory oversight.’
development of artificial intelligence. This led him to stress the importance of developing AI safely, a field in which he is ‘very close to the cutting edge.’ It was apparent in his manner, however, that this concept both fascinated and terrified him simultaneously. In Musk’s own words, ‘AI is much more dangerous than nukes,’ and requires a ‘regulatory oversight.’

 ‘parasols,’ in outer space in a ring around the planet to deflect the sun’s rays. In addition to the exorbitant costs associated with setting up these mirrors, scientists believe that side effects could include: altered weather patterns, a shift in the ice coverage at the poles and a change in the ocean currents.
‘parasols,’ in outer space in a ring around the planet to deflect the sun’s rays. In addition to the exorbitant costs associated with setting up these mirrors, scientists believe that side effects could include: altered weather patterns, a shift in the ice coverage at the poles and a change in the ocean currents.